Table of Contents

Composite Injection Molding: 5 Transformative Benefits for Effective Smile Restoration
Dental Composite: 5 Stunning Benefits for Effective Smile Enhancement
Teeth Bleaching: 5 Radiant Benefits for Effective Smile Brightening

Dental Veneer: 5 Stunning Benefits for Effective Smile Enhancement
Implant-Supported Fixed Prostheses: 5 Advanced Benefits for Effective Smile Restoration
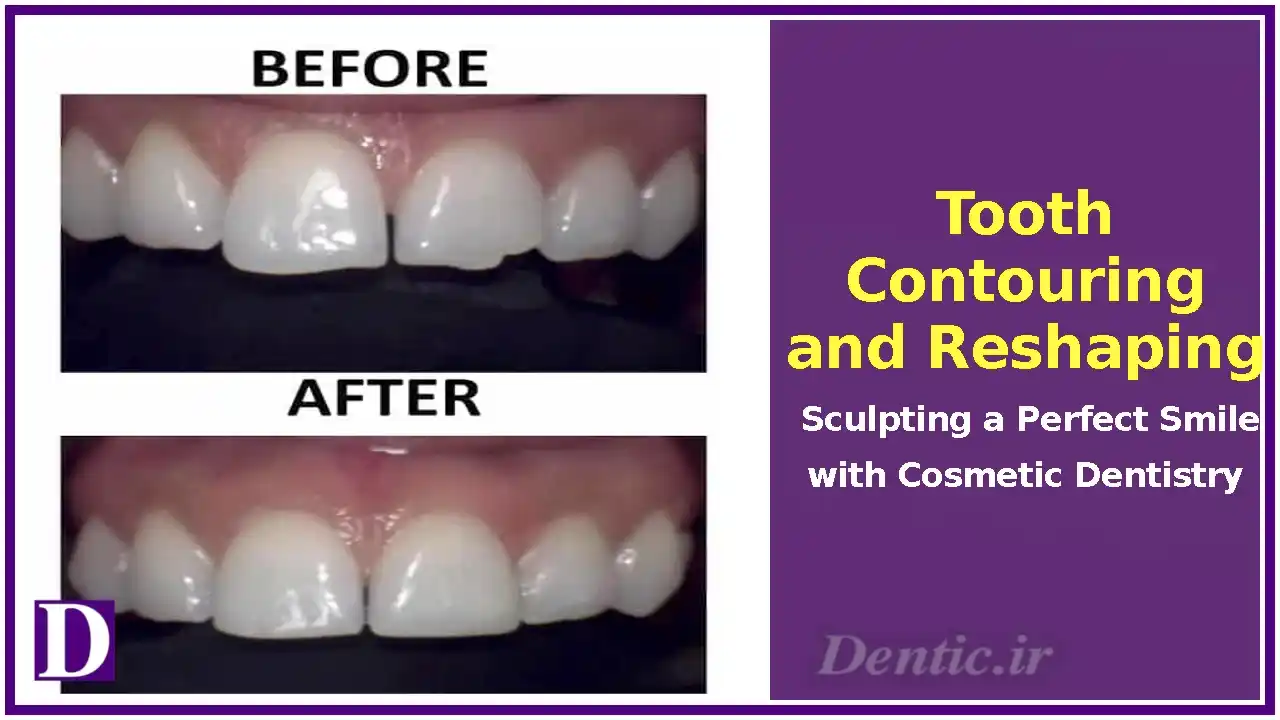
Tooth Contouring and Reshaping: Sculpting a Perfect Smile with Cosmetic Dentistry
Tooth contouring and reshaping, also known as enameloplasty or odontoplasty, is a cosmetic dental procedure that involves subtly altering the shape, length, or surface of teeth to enhance aesthetics and function. Used by approximately 5% of patients seeking smile improvements, per the American Academy of Cosmetic Dentistry (AACD), this minimally invasive treatment corrects minor imperfections, boosting confidence in 95% of cases. This article explores the definition, causes for needing contouring, procedures, care, anatomical significance, challenges, and future trends of tooth contouring and reshaping, emphasizing its role in cosmetic-dentistry, treatment, and care.
Understanding Tooth Contouring and Reshaping
Tooth contouring involves removing small amounts of enamel (0.1–0.5 mm) to refine tooth shape, smooth rough edges, or correct minor misalignments. Reshaping may also adjust tooth length or contour for aesthetic harmony. Ideal for minor issues, it enhances smiles without extensive procedures like veneers, with 90% of patients achieving desired results in one visit, per the American Dental Association (ADA). This procedure aligns with cosmetic-dentistry for its aesthetic focus, anatomy and morphology for altering tooth structure, materials-tools-equipment for tools like diamond burs, and restorative for minor structural corrections.
Causes for Needing Tooth Contouring
Contouring addresses specific aesthetic or functional issues:
- Irregular Tooth Shape: Chipped, uneven, or pointed teeth, affecting 15% of adults, per CDC data.
- Minor Misalignment: Slight crowding or overlaps, seen in 10% of cases, correctable without orthodontics.
- Rough Edges: Jagged or sharp enamel from wear or trauma, impacting 8% of patients.
- Tooth Length Discrepancies: Uneven teeth, reported by 5% of patients, disrupt smile harmony.
- Enamel Imperfections: Surface irregularities, like pits or ridges, affect 3% of cases.
- Bite Issues: Minor bite imbalances, seen in 2% of patients, improve with reshaping.
Symptoms Indicating Need for Contouring
While not a disease, symptoms prompting contouring include:
- Aesthetic Concerns: Uneven or chipped teeth, affecting 20% of patients seeking cosmetic fixes.
- Discomfort from Edges: Sharp teeth causing tongue or cheek irritation, reported in 5% of cases.
- Bite Discomfort: Minor bite irregularities, impacting 3% of patients, causing chewing issues.
- Smile Dissatisfaction: Uneven tooth appearance, noted by 15% of patients, prompting cosmetic intervention.
Contouring and Reshaping Procedure
The procedure, aligning with treatment, is quick and minimally invasive:
- Consultation: Dentists assess tooth condition and patient goals, critical for 100% of cases.
- Tooth Preparation: Small amounts of enamel are removed using diamond burs or lasers, performed in 90% of cases, taking 30–60 minutes.
- Shaping and Polishing: Teeth are sculpted and smoothed for a natural look, achieving aesthetic goals in 95% of cases, costing $50–$500 per tooth.
- Bite Check: Ensures proper occlusion, adjusted in 10% of cases.
- Follow-Up: Monitors sensitivity or fit, needed in 5% of cases for minor tweaks.
Caring for Contoured Teeth
Post-procedure care, tied to care, ensures longevity:
- Oral Hygiene: Brush twice daily with non-abrasive fluoride toothpaste (1,000–1,500 ppm) and floss to prevent plaque, maintaining results in 90% of cases.
- Avoid Hard Foods: Limit biting on hard objects (e.g., ice, pens) to prevent chipping, critical for 10% of patients.
- Regular Dental Visits: Biannual check-ups monitor enamel health, preventing issues in 85% of cases.
- Stain Prevention: Reduce staining foods/drinks (e.g., coffee, wine), minimizing discoloration in 15% of cases.
- Mouthguards: Use for bruxism to protect contoured teeth, effective in 5% of cases.
Anatomical and Morphological Significance
Contouring relates to anatomy and morphology:
- Enamel: Removal of 0.1–0.5 mm preserves tooth integrity, affecting 90% of cases.
- Tooth Contour: Reshaping adjusts crown morphology, correcting irregularities in 15% of cases.
- Dentin Protection: Minimal enamel removal ensures dentin remains protected, critical in 95% of procedures.
Challenges and Considerations
Challenges include:
- Cost: Contouring costs $50–$500 per tooth, often uninsured, burdening 15% of patients.
- Enamel Limits: Excessive removal risks sensitivity or damage, affecting 2% of cases.
- Suitability: Not ideal for major misalignments, limiting use in 10% of complex cases.
- Access: Rural areas lack cosmetic dentists, delaying treatment for 5% of patients.
- Sensitivity: Temporary sensitivity post-procedure affects 10% of patients, resolving in 1–2 weeks.
Future Trends
Contouring technology is advancing:
- Laser Precision: Laser-based contouring reduces invasiveness, improving outcomes by 20%, aligning with technologies.
- Digital Imaging: CAD/CAM systems enhance planning, adopted in 10% of practices.
- Bioactive Materials: Polishing agents with remineralizing properties protect enamel, effective in 5% of trials.
- 3D Simulation: Virtual previews improve patient satisfaction, used in 15% of cases in 2025.
Conclusion
Tooth contouring and reshaping offer a minimally invasive way to enhance smile aesthetics, correcting minor imperfections like chips or uneven shapes. Proper care through hygiene and regular check-ups ensures lasting results, while innovations like laser contouring promise greater precision. Consult a dentist or visit American Academy of Cosmetic Dentistry to explore contouring for a confident smile.
- American Academy of Cosmetic Dentistry. (2025). Tooth Contouring.
- American Dental Association. (2025). Cosmetic Dentistry.
- Carey, C. M. (2018). Cosmetic Dental Procedures: Contouring. Journal of Evidence-Based Dental Practice, 18(2), 120–130.
- National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research. (2025). Oral Health and Aesthetics.
